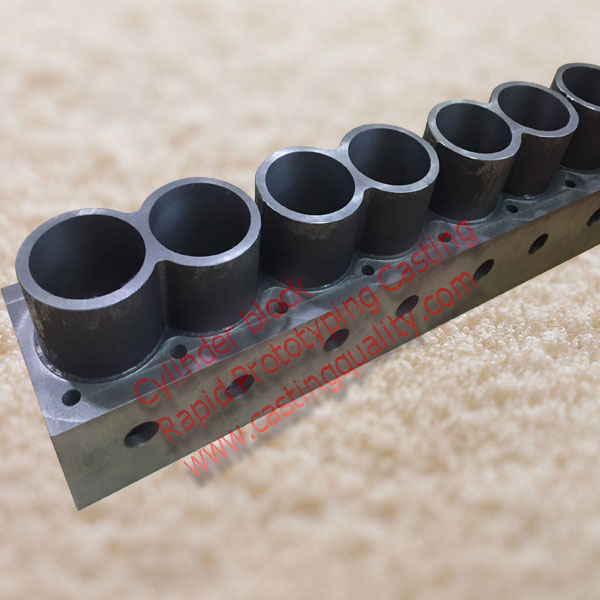
Ductile Iron, also known as spheroidal or nodular iron, is described as cast iron in which the graphite is present as spheroids, instead of flakes as in gray iron or temper carbon nodules as in malleable iron. Ductile iron is most popular metal material. ww.castingquality.com
Reference Casting Standards:
SAE J434: Automotive Ductile (Nodular) Iron Castings
Ductile Iron castings can be produced in Casting Quality Industrial:
- Sand Casting
- Shell Casting
- Lost Form Casting
Our Services
- Sand Casting
Casting Quality focus on Metal Parts industry, we provide professional service in Metal Casting field.
Sand Casting is a popular metal form method, are suitable for all materiel, such as grey iron, ductile iron, malleable iron, carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum and bronze.
- Investment Casting
also named as precision lost wax casting, mainly suitalbe for carbon steel and stainless steel parts. We also provide grey iron and ductile iron and aluminum and bronze parts by investment casting. It can achieve the best appearance with good tolerance
- Shell Casting
Shell casting method is a good option to replace investment casting and sand casting. the quality is better than sand casting parts, suitable for bulk production.
- CNC Machining
CNC Milling, CNC turning with 5 xix CNC center, we provide precision machining for all castings based on customers design drawings.
- CAD Design
Mechanical Design service based on customers requirement, our software is Solidworks and AutoCAD.
- Tools/Mold Design
Mould design and production will be served for metal casting ad plastic injection industry. Based on our more than 10 years experience, we supply professional molds for our customers in Europe and North American.
Ductile iron standard grades in SAE J434:
| Casting Grade | Typical Hardness Range (MPa) | Description | Relative Wall Thickness | Tensile Strength, min | Yield Strength, min | Elongation, min | ||
| Mpa | Ksi | Mpa | Ksi | % | ||||
| SAE J434 D400 (D4018) | 143-170HBW (1402-1667) or as agreed | Ferrite | <=20 | 400 | 58 | 275 | 40 | 18 |
| >20-<=40 | 260 | |||||||
| >40-<=60 | 250 | |||||||
| SAE J434 D450 (D4512) | 156-217HBW (1530-2128) or as agreed | Ferrite Pearlite | <=20 | 450 | 65 | 310 | 45 | 12 |
| >20-<=40 | 295 | |||||||
| >40-<=60 | 285 | |||||||
| SAE J434 D500 (D5006) | 187-229 HBW (1834-2246) or as agreed | Ferrite Pearlite | <=20 | 500 | 73 | 345 | 50 | 6 |
| >20-<=40 | 330 | |||||||
| >40-<=60 | 320 | |||||||
| SAE J434 D550 (D5504) | 217-269 HBW (2128-2638) or as agreed | Pearlite Ferrite | <=20 | 550 | 80 | 380 | 55 | 4 |
| >20-<=40 | 365 | |||||||
| >40-<=60 | 350 | |||||||
| SAE J434 D700 (D7003) | 241-302 HBW (2363-2961) or as agreed | Pearlite | <=20 | 700 | 102 | 450 | 65 | 3 |
| >20-<=40 | 435 | |||||||
| >40-<=60 | 425 | |||||||
| SAE J434 D800 | 255-311 HBW (2501-3050) or as agreed | Pearlite or Tempered Martensite | <=20 | 800 | 116 | 480 | 70 | 2 |
| >20-<=40 | 465 | |||||||
| >40-<=60 | 455 | |||||||
| SAE J434 DQ&T | Range specified by agreement | Tempered Martensite | A wide variety of properties are possible. Minimum properties are specified by agreement between manufacture and purchaser | |||||
SAE J434 Ductile Iron Heat treatment requirement: www.castingquality.com
Generally the heat treatment of castings and specimens in SAE J434 in order to meet the hardness or mechanical property requirements is permissible only with the express approval of the casting purchaser.
But the typical microstructures of the grade of ductile iron as follows (for reference only):
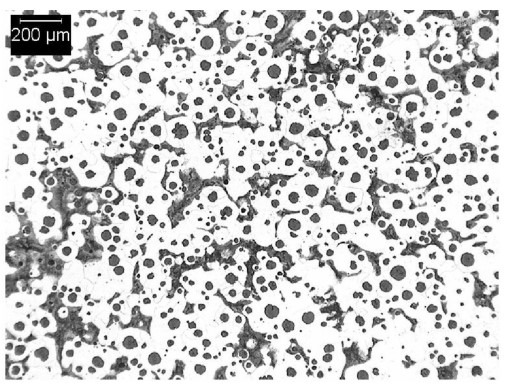
D400(D4018) is a ferritic ductile iron most commonly made by annealing.
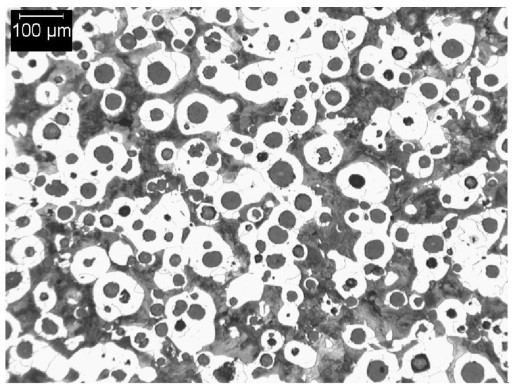
D450 (D4512) is ferritic ductile iron supplied either as cast or heat treated.
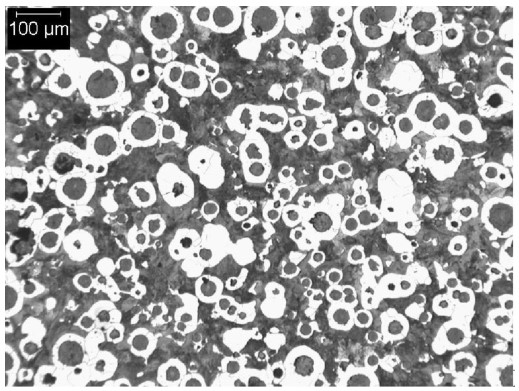
D500 (D5006) is ferritic-pearlite ductile iron supplied either as cast or heat treated.
D550 (D5504) is pearlitic-ferritic ductile iron supplied either as cast or heat treated.
D700 (D7003) is either as cast or qir quenched to a specified hardness range.
D800 is either as cast or air or liquid quenched and tempered to a specified hardness range.
DQ&T is liquid quenched and tempered grade.
SAE J434 Microstructure:
The graphite component of the microstructure shall consist of at least 80% spheroidal graphite conforming to types I and II (per ASTM A247): 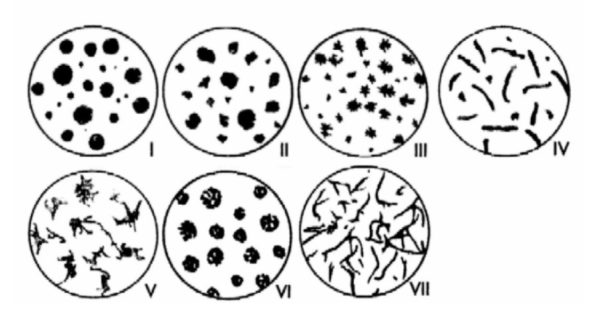
The matrix microstructure shall consist of ferrite, ferrite and pearlite, pearlite, tempered pearlite, or tempered martensite, or a combination of those.

SAE J434 D400 Typical Matrix Microstructures
SAE J434 D450 Typical Matrix Microstructures
SAE J434 D500 Typical Matrix Microstructures
SAE J434 D550 Typical Matrix Microstructures
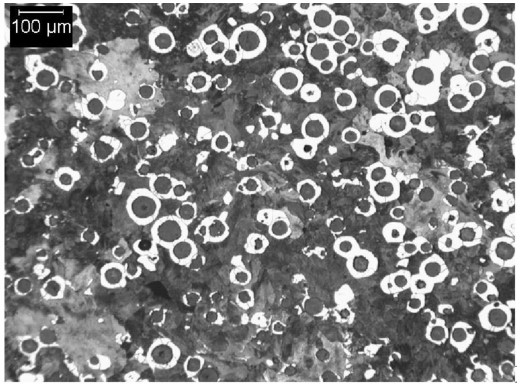
SAE J434 D700 Typical Matrix Microstructures
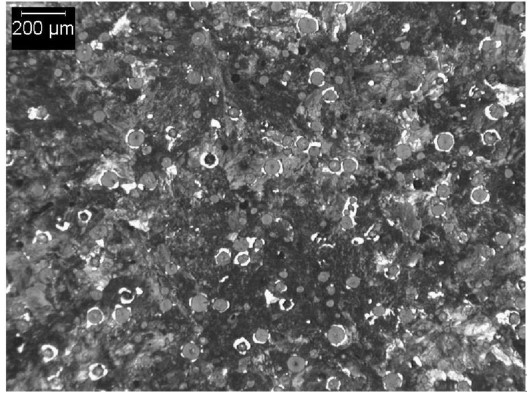
SAE J434 D800 Typical Matrix Microstructures
Chemical Composition in SAE J434 ( for information only): The typical chemical composition of unalloyed iron generally confirms to following range. The spheroidal graphite structure is produced by alloying the molten iron with small amounts of one or more elements such as magnesium or cerium. The matrix microstructure may be controlled by addition of other alloying elements, such as: copper, tin, nickel, chromium and molybdenum.
Carbon: 3.20-4.10%
Silicon: 1.80-3.00%
Manganese: 0.10-1.00%
Phosphorus: 0.050% max
Sulfur: 0.035% max
Magnesium: 0.025-0.060%
Typical un-notched Charpy impact energy properties are from low residual element content iron, impact values are affected by microstructure and section size:
| Grade | TYPICAL IMPACT VALUE (For information only) | |
| JOULES | FT-LBS | |
| SAE J434 D400 (D4018) | 120 | 90 |
| SAE J434 D450 (D4512) | 80 | 60 |
| SAE J434 D500 (D5006) | 54 | 40 |
| SAE J434 D550 (D5504) | 40 | 30 |
| SAE J434 D400 (D4018) | 27 | 20 |
SAE J434 Ductile Iron Typical Casting Application
Machinery, valve, truck, railway, gearbox, flywheels etc.
D400 (D4018) is used in moderately stressed parts requiring high ductility and good machinability.
D450 (D4512) and D500 (D5006) are used for moderately stressed parts where machinability is less important.
D550 (D5504) is used for more highly stressed parts.
D700 (D7003) and D800 are used where high strength and/or improved wear resistance are required and where selective hardening is to be employed.
DQ&T is used where the uniformity of a heat treated material is required to control the range of mechanical properties or machinability.


 PDF VIEW
PDF VIEW




